The arrows in the graphic below all have the same length and direction. This observation to the eye can also be expressed in numbers: starting from the tail of any of these arrows, its tip is located \(3\) units to the right and \(1\) unit down. Thus we may take the order pair \((3,-1)\) to describe all the arrows in this vector.
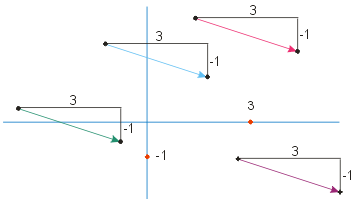
Conversely, we say that the vector \(\Vect{x} = (3,-1)\) is represented by any of the arrows in the picture above.
For example,
- if we choose \(R(2,2)\) as the tail point of an arrow representing \(\Vect{x}\), the tip of this arrow will be at \(S(2+3,2+(-1))=S(5,1)\)
- if we choose \(A(14,-6)\) as the tail point of an arrow representing \(\Vect{x}\), the tip of this arrow will be at \(B(17,-7)\)
- If we choose \(U(0,0)\) as the tail point of an arrow representing \(\Vect{x}\), the tip of this arrow will be at \(V(3,-1)\)